low end tidal co2 during cpr
Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. We compared ETCO2-directed chest compressions with chest compressions optimized to pediatric basic life support guidelines in an infant swine model to.

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram
End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement.

. Change in the end-tidal CO2 value was often the first clinical indicator that ROSC had occurred. In mmHg the PetCO2 values for those with and without ROSC after five minutes of CPR was. Our findings suggest that end-tidal CO2 monitoring may provide clinically useful information that can be.
Carbon Dioxide During the Low Flow State Initiation of CPR During CPR chest compressions along with positive pressure ventilation restore organ perfusion and oxygenation to some extent. Thus ETco 2 monitoring is a noninvasive way to measure coronary artery blood flow and return of spontaneous circulation during CPR. By measuring exhaled CO2 many types of pulmonary assessments can be made.
Evidence suggests a persistently low ETco 2 value and a widened Paco 2-to-ETco 2 gradient during CPR are associated with poor outcomes. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide Monitoring.
Leaking anesthetic circuit. 25 EtCO2 correlates well with cardiac output and rapidly drops to zero at CPA onset. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
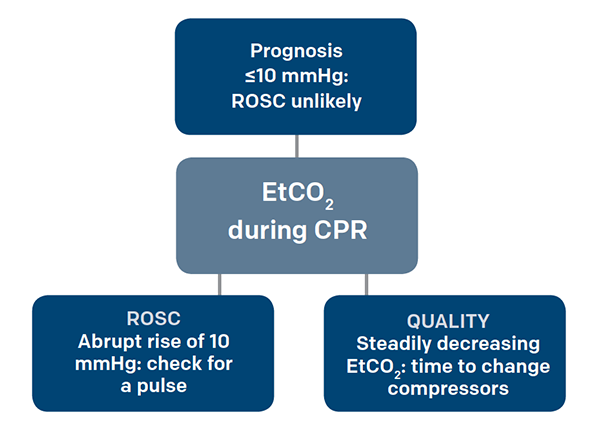
Goal is 10 mmHg during CPR. End-tidal CO2 ETCO2 detection requires air movement in and out of the lungs ventilation CO2 production from cellular metabolism and. Another use of ETco 2 monitoring is during procedural sedation and analgesia PSA.
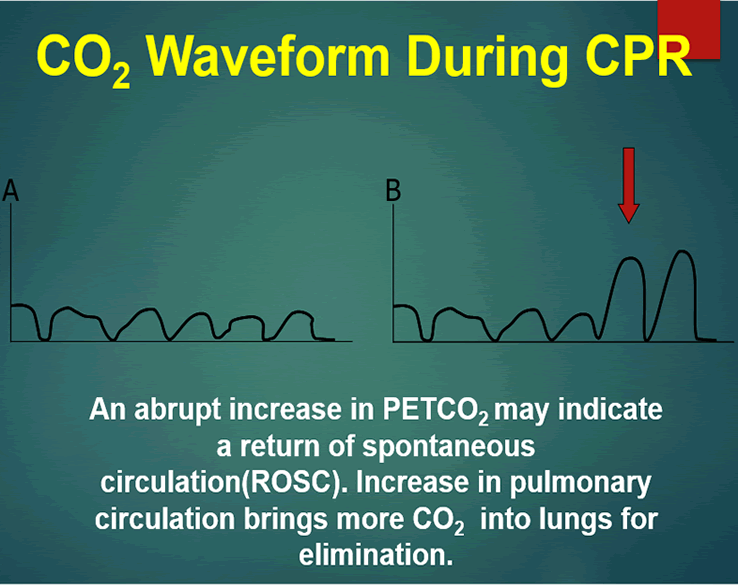
Systematic review and meta-analysis of end-tidal carbon dioxide values associated with return of spontaneous circulation during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Uses during cardiac arrest. This will cause a decrease in the ETCO2 end-tidal CO2 and this will be observable on the waveform as well as with the numerical measurement.
During CPR ETCO2 levels were initially high decreased to low levels and increased again at ROSC. 59 Additional reasons for rapid decreases include. MmHg Relate to the air we breath.
Measurement of a low ETCO 2 value 10 mmHg during CPR in an intubated patient suggests that the quality of chest compressions needs improvement. 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC. Two very practical uses of waveform capnography in CPR are.
428 153 mmHg versus 323 141 mmHg. 1 evaluating the effectiveness of chest compressions and 2 identification of ROSC. Low end tidal co2 during cpr.
Normal ETCO2 in the adult patient should be 35-45 mmHg. J Intensive Care Med. Loss of ETCO2 may be the first sign that CPR is needed.
Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists. The first sign of the return of spontaneous circulation ROSC during CPR is increase in ETCO2. End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 is a noninvasive technique which represents the partial pressure or maximal concentration of CO2 at the end of exhalation.
78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. Normal value is 35-45 mmHg. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 correlates with systemic blood flow and resuscitation rate during cardiopulmonary resuscitation CPR and may potentially direct chest compression performance.
Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition. The end-tidal CO2 concentration increased immediately in all patients who had ROSC from 17 - 06 to 46 - 14 then gradually returned to a new baseline 31 - 09. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs.
These levels of CO 2 were consistent with effective chest compression generating reasonable pulmonary blood flow justifying continuation of resuscitation. A low P a CO2 level is correlated with increased risk of cerebral edema in children with DKA. Abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful.
Ensure proper rate approximately 100min Ensure proper depth with adequate releaserecoil of thorax 12 thorax or minimum 25 inches Persistently low EtCO. Here are five things you should know about waveform capnography in cardiac arrest. 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC.
Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing. More Than Just a Number.
What should end-tidal CO2 be during CPR. End-tidal carbon dioxide cannot be used to rule out severe injury in patients meeting the criteria for trauma care. 423 20 mmHg versus 34 255 mmHg.
End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 monitoring is recommended for intubated patients at risk of CPA I-A. 4 to 5 CO2 PetCO2 vs. Throughout the resuscitation end-tidal CO 2 was consistently in the 28-36 mmHg range during VFCPR.
Graphically this difference in ROSC vs non-ROSC PetCO2 for both groups appeared to be even greater at ten minutes.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Use End Tidal Capnography For Placing Orogastric Nasogastric Tubes And Cpr Page 2 Of 4 Acep Now Page 2

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi
Cpr Mobile Code Stand With Capnograph Capnography

Capnography During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Current Evidence And Future Directions
What Is Capnography Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education

Reversible Causes Of Low Etco2 In Cpr Criticalcarenow

3 Waveform Capnography Showing Changes In The End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

The Role Of Etco2 In Termination Of Resuscitation Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News